Introduction
A recent survey found that 62% of millennials are turning to ancient philosophies like Stoicism for guidance in navigating modern life's complexities. This statistic resonates with me personally. Last year, I faced a career setback that left me feeling lost and anxious. It was then that I stumbled upon Stoic teachings, which provided a framework for resilience and clarity. This experience sparked my journey into Stoicism, leading me to create this comprehensive guide. We'll explore Stoicism's foundations, core practices, modern applications, and future relevance. Whether you're a curious newcomer or a seasoned practitioner, this guide aims to deepen your understanding and application of Stoic principles in today's world.
Stoicism originated in ancient Greece around 300 BCE, emphasizing virtue, reason, and self-control. The philosophy has experienced a resurgence in popularity in recent years, with many finding its principles particularly relevant to our fast-paced, often chaotic modern lives. According to a "Report on Stoic Week 2022" by Modern Stoicism, participants experienced a significant increase in wellbeing measures after practicing Stoic principles for just one week.
This renewed interest isn't limited to personal development circles. Olympic gold medalist Mark Tuitert recently released a book on applying Stoic principles to achieve peak performance, as reported by "McKinsey & Company". Tuitert emphasizes how Stoicism can help separate the pursuit of goals from happiness, leading to a more fulfilling life. This application of ancient wisdom to modern challenges exemplifies the versatility and enduring relevance of Stoic philosophy.
Table of Contents
- The Foundations of Stoic Philosophy
- Origins and Evolution of Stoicism
- The Four Cardinal Virtues
- Stoicism vs. Other Philosophies
- Core Stoic Practices for Daily Life
- Memento Mori: Embracing Mortality
- Negative Visualization
- The Dichotomy of Control
- Modern Stoicism: Adaptations and Critiques
- Stoicism in Leadership and Business
- Stoicism and Mental Health
- Criticisms and Limitations of Stoicism
- The Future of Stoicism
- Stoicism in the Digital Age
- Environmental Stoicism
- Stoicism and Global Citizenship
Key Takeaways
- Stoicism offers practical tools for resilience and ethical living in modern times
- Core Stoic practices include negative visualization, focusing on what's within our control, and embracing our mortality
- Modern applications of Stoicism extend to business leadership, mental health, and environmental sustainability
- While powerful, Stoicism has limitations and critics, particularly regarding its approach to emotions and systemic issues
- The future of Stoicism involves adapting ancient wisdom to emerging challenges in technology, global citizenship, and environmental stewardship
The Foundations of Stoic Philosophy
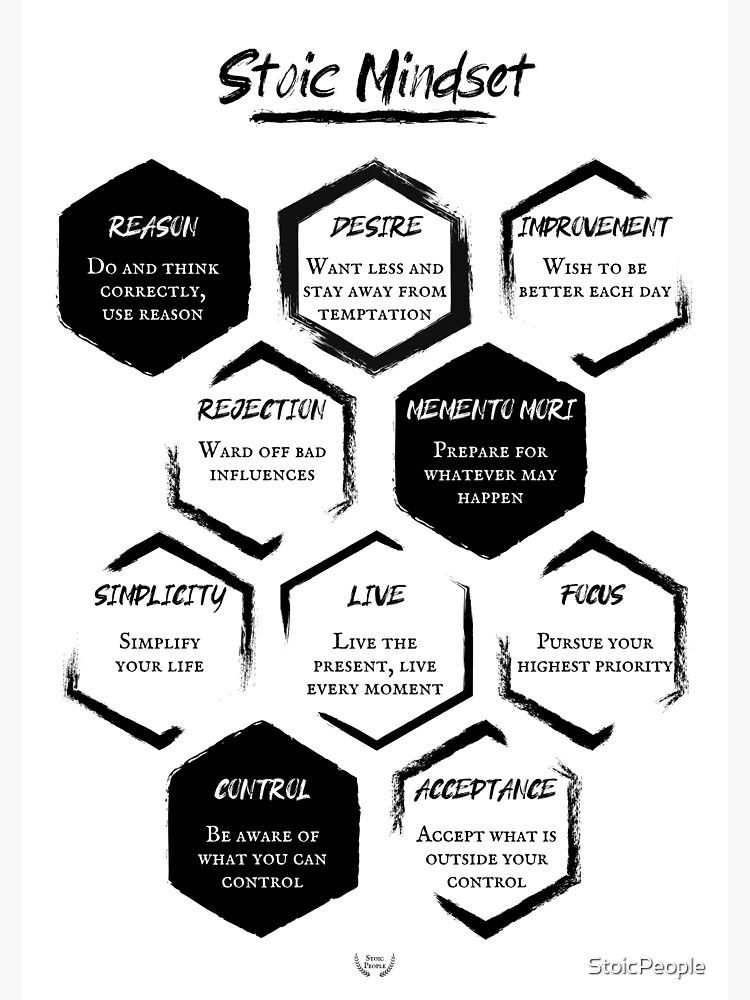
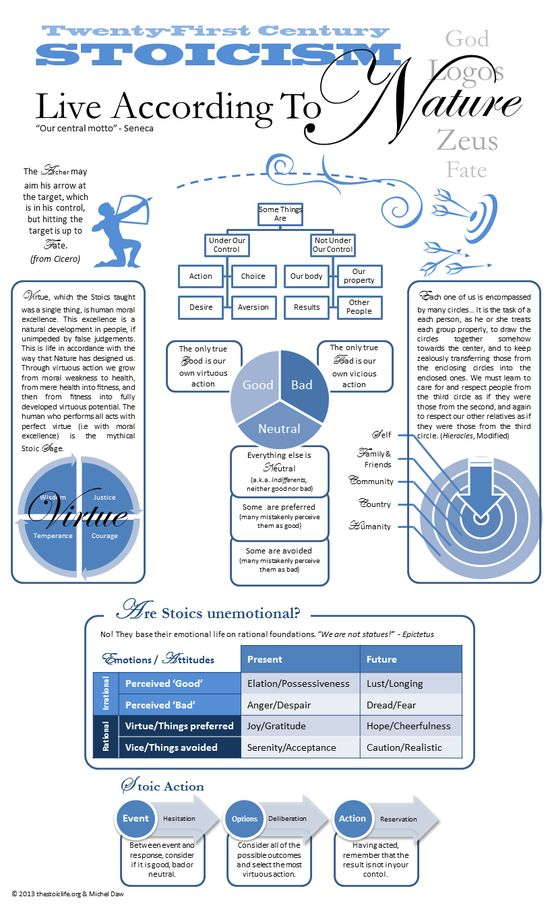
Stoicism, at its core, teaches us to focus on what's within our control and accept what isn't. It's a philosophy that has profoundly impacted my own life, especially during times of uncertainty. When I lost my job last year, I found myself spiraling into anxiety about the future. Applying Stoic principles helped me regain perspective, focusing my energy on what I could control - my skills, my attitude, and my job search efforts - rather than worrying about external factors beyond my influence.
The philosophy encourages us to cultivate virtues like wisdom, justice, courage, and temperance. These aren't just lofty ideals but practical tools for navigating life's challenges. I've found that regularly reflecting on these virtues helps guide my decision-making, both in personal and professional contexts.
One aspect of Stoicism that I find particularly compelling is its view of the universe as a rational and interconnected system. This perspective can be incredibly comforting in times of chaos or uncertainty. It reminds us that even when things seem random or unfair, there's an underlying order to the universe. This doesn't mean passively accepting injustice, but rather approaching challenges with a sense of purpose and equanimity.
Source: redbubble.com
One of the most appealing aspects of Stoicism is its practicality. It's not just a set of abstract ideas, but a philosophy meant to be lived. Stoic practices can be applied to everything from managing stress at work to dealing with personal relationships. For instance, when facing a difficult work situation, a Stoic approach would involve identifying what aspects you can control (your own actions and reactions) and what you cannot (your colleagues' behaviors or company policies). By focusing your energy on the former and accepting the latter, you can navigate the situation more effectively and with less emotional turmoil.
It's important to note that while Stoicism emphasizes emotional regulation, it doesn't advocate for suppressing emotions entirely. Rather, it encourages us to examine our emotional reactions and respond thoughtfully rather than reactively. This nuanced approach to emotions is something I've found particularly valuable in my own life, helping me maintain composure in high-stress situations without becoming cold or detached.
Origins and Evolution of Stoicism
Stoicism's journey from ancient Greece to modern-day applications is a fascinating tale of philosophical evolution. The philosophy was founded in Athens by Zeno of Citium around 300 BCE. It got its name from the Stoa Poikile, a painted porch where Zeno taught. I find it intriguing how a philosophy that began in such a specific physical location has spread to influence thinkers and practitioners worldwide.
Over time, Stoicism evolved and adapted, spreading throughout the Greek and Roman world. Roman thinkers like Seneca, Epictetus, and Marcus Aurelius played crucial roles in refining and popularizing Stoic ideas. Their writings continue to be widely read and studied today. I've personally found great wisdom in Marcus Aurelius's "Meditations," a collection of personal writings that offer insights into how a powerful leader applied Stoic principles in his daily life.
What's particularly interesting is how Stoicism has influenced various fields beyond philosophy. Its ideas have shaped cognitive behavioral therapy, mindfulness practices, and even modern self-help literature. This broad impact demonstrates the enduring relevance of Stoic principles. According to the Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy, Stoicism's influence extends to various fields including psychology, ethics, and political theory.
Era
Key Figures
Major Contributions
Early Stoa (300-129 BCE)
Zeno, Cleanthes, Chrysippus
Foundational principles, Logic, Physics
Middle Stoa (129-30 BCE)
Panaetius, Posidonius
Adaptation to Roman culture, Ethics
Late Stoa (30 BCE - 180 CE)
Seneca, Epictetus, Marcus Aurelius
Practical applications, Personal ethics
Zeno of Citium: The Founder's Journey
Zeno's personal experiences, including a life-altering shipwreck, profoundly influenced the development of Stoic philosophy. His teachings on the Stoa Poikile laid the groundwork for a philosophical tradition that would span centuries. I find Zeno's story particularly inspiring as it demonstrates how personal adversity can lead to profound insights and positive change.
After losing everything in a shipwreck, Zeno found himself in Athens, where he became fascinated by philosophy. This personal tragedy became the catalyst for a philosophical revolution. It's a powerful reminder that sometimes our greatest setbacks can lead to our most significant growth and contributions.
On the Stoa Poikile, Zeno developed and shared his ideas about virtue, reason, and living in harmony with nature. These concepts formed the core of Stoic philosophy and continue to resonate with people today. Zeno's teachings emphasized the importance of inner peace and self-control. He believed that true happiness comes from within, not from external circumstances. This idea remains a cornerstone of Stoic thought and one that I've found particularly valuable in my own life.

Source: wikipedia.org
From a different perspective, some scholars argue that Zeno's emphasis on self-control and inner peace might have been influenced by the political instability of his time. In an era of frequent wars and social upheaval, the idea of finding stability within oneself rather than external circumstances would have been particularly appealing. This historical context adds depth to our understanding of Stoicism's origins and its enduring appeal in times of uncertainty.
Roman Stoicism: Seneca, Epictetus, and Marcus Aurelius
The Roman Stoics - Seneca, Epictetus, and Marcus Aurelius - played pivotal roles in refining and popularizing Stoic principles. Their contributions made Stoicism more accessible and applicable to everyday life. I've found their writings to be a rich source of practical wisdom, offering insights that are remarkably relevant to modern challenges.
Seneca, a wealthy statesman and playwright, wrote extensively on Stoic ethics. His letters and essays offer practical advice on everything from dealing with anger to finding contentment in life. Seneca's writings are particularly relevant for those grappling with the challenges of success and power. I've often turned to his essays when facing ethical dilemmas in my professional life.
Epictetus, born a slave, became one of the most influential Stoic teachers. His "Handbook" (Enchiridion) provides concise, powerful guidance on living a Stoic life. Epictetus emphasized the importance of focusing on what's within our control - our thoughts and actions. This principle has been a game-changer for me, helping me navigate stressful situations with greater calm and clarity.
Marcus Aurelius, the Roman Emperor, is perhaps the most famous Stoic. His personal journal, "Meditations," offers insights into how a powerful leader applied Stoic principles in his daily life. Marcus's writings remind us that Stoicism is relevant for people from all walks of life. I find it incredibly inspiring that a Roman Emperor faced many of the same internal struggles we do today, and used philosophy to navigate them.
A study published in the Journal of Positive Psychology found that reading Stoic texts for just one week led to significant improvements in resilience and life satisfaction among participants. This research underscores the practical benefits of engaging with Stoic philosophy, even in our modern context.
Consider Marcus Aurelius, who as Roman Emperor, faced immense pressures and challenges. In his personal journal, later published as "Meditations," he repeatedly reminds himself to focus on what he can control, to act with virtue, and to view obstacles as opportunities. For instance, when dealing with difficult people, he writes: "Begin each day by telling yourself: Today I shall be meeting with interference, ingratitude, insolence, disloyalty, ill-will, and selfishness..." This practice helped him maintain equanimity in the face of adversity.
From a different angle, it's worth noting that the Roman Stoics' emphasis on duty and civic responsibility was partly a response to the political realities of the Roman Empire. Their teachings on how to live virtuously within a complex and often corrupt system offer valuable insights for navigating modern institutional challenges. This historical context adds depth to our understanding of Stoic philosophy and its practical applications in different societal structures.
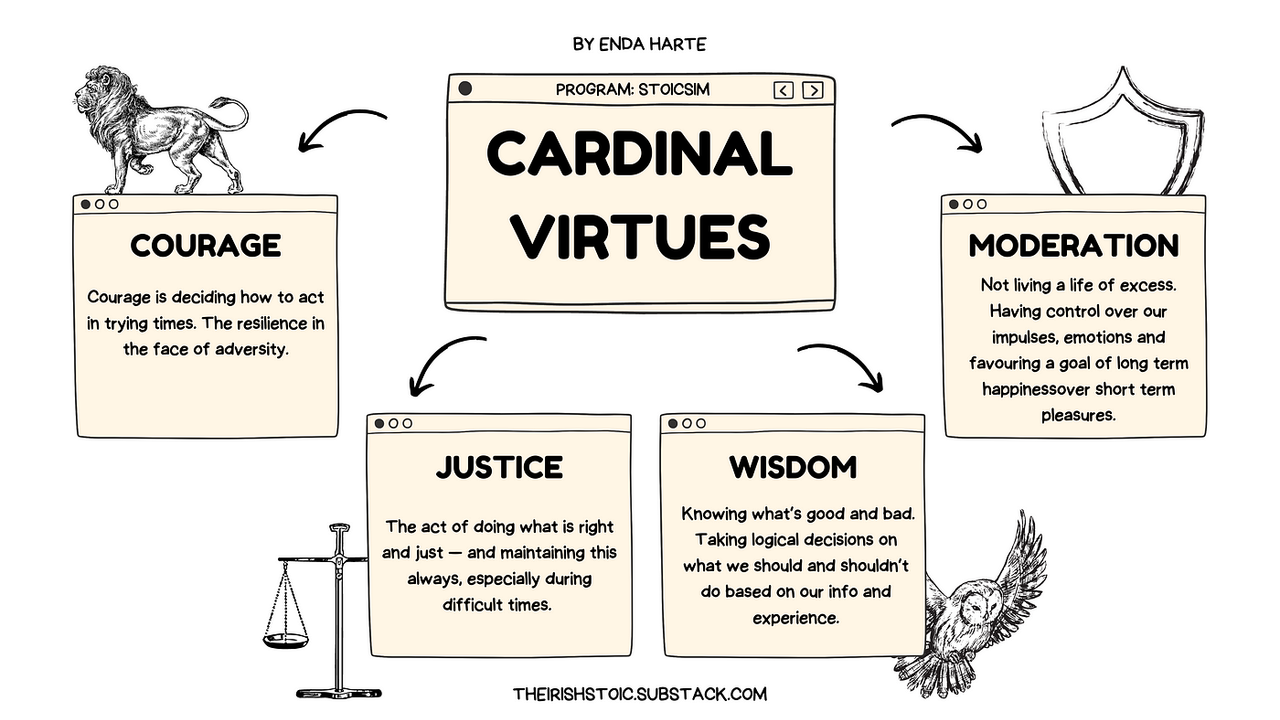
The Four Cardinal Virtues
The four cardinal virtues - Wisdom, Justice, Courage, and Temperance - form the ethical foundation of Stoicism. Understanding and cultivating these virtues is key to living a fulfilling life according to Stoic principles. In my own journey with Stoicism, I've found that regularly reflecting on these virtues provides a powerful framework for personal growth and ethical decision-making.
Wisdom, in Stoic terms, isn't just about accumulating knowledge. It's about understanding what's truly important in life and making sound judgments. It involves seeing things clearly and acting accordingly. I've found that cultivating wisdom often means challenging my own assumptions and biases, and being open to new perspectives.
Justice, for the Stoics, goes beyond legal definitions. It's about treating others fairly and contributing positively to society. This virtue reminds us of our interconnectedness with others. In my professional life, I've found that keeping this virtue in mind helps me make decisions that consider the broader impact on my team and organization, not just my personal gain.
Source: medium.com
Courage isn't just about physical bravery. It's about facing life's challenges with resilience and integrity. This includes standing up for what's right, even when it's difficult. I've found this virtue particularly important in navigating career challenges and personal setbacks. It's about pushing through fear and discomfort to do what's necessary and right.
Temperance is about moderation and self-control. It involves managing our desires and emotions, finding balance in all aspects of life. In our modern world of constant stimulation and instant gratification, I've found this virtue to be increasingly crucial. It guides me in making mindful choices about how I spend my time and energy.
These virtues aren't meant to be pursued in isolation. They work together, supporting and balancing each other. By striving to embody these virtues, we can navigate life's complexities with greater ease and purpose. It's important to remember that perfection isn't the goal - it's about continuous improvement and striving to live more virtuously each day.
From a different perspective, some modern ethicists argue that the Stoic virtues, while valuable, may not fully address the complexities of contemporary moral challenges. For instance, issues of global justice or environmental ethics might require additional ethical frameworks. This critique encourages us to think about how we might adapt or expand upon the Stoic virtues to address modern ethical dilemmas more comprehensively.
Practical Applications of Stoic Virtues
Stoic virtues aren't just theoretical concepts - they can be applied to real-world situations to guide decision-making and behavior. In my experience, incorporating these virtues into daily life has led to more thoughtful choices and a greater sense of purpose. Let's explore some practical ways to incorporate these virtues into daily life.
In the workplace, wisdom might involve making thoughtful decisions based on long-term consequences rather than short-term gains. I've found this particularly valuable when facing ethical dilemmas or strategic decisions. Justice could mean treating colleagues fairly and advocating for equitable policies. This might involve speaking up against discriminatory practices or ensuring that credit is given where it's due.
Courage might be needed when standing up to workplace bullying or unethical practices. I remember a situation where I had to confront a superior about a questionable business practice. It was uncomfortable, but embodying the Stoic virtue of courage helped me navigate the situation with integrity.
Temperance could help in managing work-life balance and avoiding burnout. I've learned to set boundaries on my work hours and prioritize self-care, which has significantly improved my overall well-being and productivity.
A survey by the Harvard Business Review found that 79% of business leaders believe that applying philosophical principles like Stoicism can lead to better decision-making and more ethical business practices. This statistic underscores the growing recognition of Stoicism's relevance in professional settings.
In a recent interview with Fast Company, Olympic gold medalist Mark Tuitert discussed how Stoic principles helped him focus on preparation rather than outcomes. He states, "Stoics focus their energy not on winning, but on making the right choices." This approach can be applied in various professional settings to reduce stress and improve performance.
In personal relationships, wisdom could guide us in communicating effectively and resolving conflicts. Justice might involve being a supportive friend or partner, while respecting boundaries. Courage might be required to have difficult but necessary conversations. Temperance could help in managing emotions during disagreements.
These are just a few examples. The key is to regularly reflect on these virtues and look for opportunities to practice them in your daily life. It's not about perfection, but about continuous improvement and striving to live more virtuously each day.
Balancing Virtues in Modern Dilemmas
Modern life often presents complex ethical situations where Stoic virtues can provide guidance. Balancing these virtues requires ongoing reflection and practice. The goal isn't perfection, but continuous improvement in applying these principles to life's challenges.
Consider a scenario where you discover a colleague is cutting corners on a project. Wisdom would involve understanding the full situation. Justice might push you to report the issue. Courage could be needed to confront the colleague directly. Temperance would help you approach the situation calmly and avoid overreacting.
In the realm of social media, wisdom might guide you in discerning reliable information from misinformation. Justice could involve using your platform responsibly. Courage might be needed to stand up against online bullying. Temperance could help in managing your time spent on these platforms.
Modern Dilemma
Relevant Virtues
Stoic Approach
Social Media Use
Wisdom, Temperance
Mindful consumption, focus on meaningful connections
Climate Change
Justice, Courage
Consider impact on future generations, take action
Workplace Ethics
Wisdom, Justice, Courage
Stand up for what's right, consider long-term consequences
Personal Health
Temperance, Wisdom
Practice moderation, make informed choices
When facing environmental issues, wisdom could help in understanding the complexities of climate change. Justice might involve considering the impact of your actions on future generations. Courage could be needed to make lifestyle changes. Temperance might guide you in finding sustainable consumption habits.
From a different perspective, some critics argue that strictly adhering to Stoic virtues might sometimes lead to inflexibility in complex situations. They suggest that while these virtues provide a solid ethical foundation, we should also remain open to other ethical frameworks and be willing to adapt our approach based on specific contexts. This viewpoint encourages a more nuanced application of Stoic principles in modern dilemmas.
Stoicism vs. Other Philosophies
While Stoicism shares some commonalities with other philosophical traditions, it has unique aspects that set it apart. Comparing Stoicism with other philosophies can deepen our understanding of its distinctive features and help us appreciate its unique contributions to ethical and practical living.
Stoicism and Epicureanism, both Hellenistic philosophies, differ in their views on pleasure. While Epicureanism sees pleasure as the highest good, Stoicism focuses on virtue as the path to happiness. Stoics believe that pursuing virtue leads to true contentment, regardless of external circumstances.
Compared to existentialism, Stoicism offers a more structured approach to finding meaning in life. While existentialists emphasize individual freedom and responsibility in creating meaning, Stoics believe in aligning oneself with a rational, universal order.
Source: reddit.com
Stoicism shares some similarities with Buddhism, particularly in its emphasis on mindfulness and detachment from external events. However, Stoicism doesn't reject the material world entirely and encourages active participation in society.
Unlike nihilism, which often leads to a sense of meaninglessness, Stoicism provides a framework for finding purpose and living ethically. It offers practical tools for dealing with life's challenges rather than succumbing to despair.
These comparisons help illustrate Stoicism's unique blend of practicality and ethical rigor. It offers a middle path between extreme asceticism and hedonism, providing a balanced approach to living well.
Stoicism and Eastern Philosophy: Parallels and Divergences
Stoicism shares intriguing similarities with Eastern philosophies like Buddhism and Taoism, but also has significant differences. Exploring these parallels and divergences offers insights into the universal and unique aspects of Stoic thought.
Both Stoicism and Buddhism emphasize the importance of managing one's desires and emotions. They share the view that much of human suffering comes from attachments and false perceptions. However, their approaches differ. Stoicism focuses on using reason to overcome these challenges, while Buddhism often emphasizes meditation and mindfulness practices.
Stoicism and Taoism both advocate for living in harmony with nature. But while Taoism often emphasizes non-action (wu wei) and going with the flow, Stoicism encourages active engagement with the world, guided by reason and virtue.
The concept of acceptance is central to both Stoicism and many Eastern philosophies. However, Stoic acceptance is more about acknowledging reality to take appropriate action, rather than passive resignation.
Consider the concept of acceptance in both Stoicism and Buddhism. A Buddhist might practice mindfulness meditation to cultivate acceptance of present moment experiences. A Stoic, on the other hand, might use rational reflection to accept unchangeable circumstances while focusing on what can be changed. Both approaches aim for inner peace, but through different methods.
Unlike many Eastern philosophies, Stoicism places a strong emphasis on civic duty and social engagement. Stoics believe in actively contributing to society, while many Eastern traditions focus more on individual spiritual development.
These comparisons reveal that while Stoicism shares some universal insights with Eastern thought, it offers a unique Western approach to dealing with life's challenges. It combines elements of acceptance and detachment with active engagement and ethical living.
Core Stoic Practices for Daily Life
Stoicism isn't just a set of ideas - it's a practical philosophy meant to be lived. Incorporating key Stoic practices into your daily routine can cultivate resilience, clarity, and ethical living. I've found these practices to be transformative in my own life, helping me navigate challenges with greater equanimity and purpose.
Starting the day with a morning meditation has been a game-changer for me. It's a time to reflect on my values and set intentions for the day ahead. This practice helps me stay grounded and focused, even when faced with unexpected challenges.
Another powerful practice is journaling. Writing down your thoughts and experiences through a Stoic lens can provide valuable insights and help reinforce Stoic principles. You might reflect on how you applied (or failed to apply) Stoic virtues throughout your day.

Source: whatisstoicism.com
Practicing gratitude is also central to Stoic thought. Regularly acknowledging the good in your life can shift your perspective and increase overall well-being. Try listing three things you're grateful for each day. I've found this practice particularly helpful during challenging times, as it reminds me of the positive aspects of life that I might otherwise overlook.
The Stoic practice of voluntary discomfort involves intentionally putting yourself in challenging situations. This might mean taking a cold shower or fasting for a day. The goal is to build resilience and remind yourself that you can handle discomfort. While it might seem counterintuitive, I've found that this practice has significantly increased my confidence in facing life's inevitable challenges.
Remember, consistency is key with these practices. Start small and gradually incorporate them into your routine. Over time, you'll likely notice significant changes in your mindset and approach to life's challenges.
Memento Mori: Embracing Mortality
Memento Mori, or "remember you must die," is a central Stoic practice that encourages contemplation of one's mortality. Far from being morbid, this practice can lead to a more purposeful and appreciative approach to life.
Reflecting on death provides perspective on life. It reminds us of the preciousness of time and the importance of living according to our values. I've found that regularly contemplating my own mortality has helped me prioritize what truly matters and let go of trivial concerns.
Memento Mori can alleviate anxiety about death. By confronting and accepting our mortality, we can reduce the fear and uncertainty that often surrounds it. This practice has helped me approach life with a sense of urgency and appreciation, rather than fear or avoidance.

Source: store.dailystoic.com
The practice motivates making the most of limited time. When we're acutely aware of life's finite nature, we're more likely to pursue what truly matters to us. I've found this awareness pushes me to take action on important goals and not put off meaningful experiences.
A study in the Journal of Positive Psychology found that regular contemplation of mortality can lead to increased life satisfaction and a greater sense of purpose. This research underscores the practical benefits of engaging with this Stoic practice.
Memento Mori doesn't mean constantly dwelling on death. Instead, it's about periodically reminding ourselves of life's finite nature. This can be as simple as reflecting on it for a few minutes each day or week.
Some people find it helpful to keep physical reminders of mortality, like artwork or small objects. Others might incorporate it into their meditation or journaling practice. The key is finding a method that works for you and helps you maintain a healthy perspective on life and death.
Digital Age Memento Mori Practices
In our technology-driven world, there are innovative ways to incorporate the practice of Memento Mori into our digital lives. These modern tools can serve as reminders of life's impermanence and encourage us to live more purposefully.
One simple approach is to set daily reminders on your phone or computer with Memento Mori-inspired messages. These can serve as brief moments of reflection amidst your busy day. I've found that even a quick notification can jolt me out of autopilot and remind me to focus on what's truly important.
There are also apps specifically designed for this purpose. Some calculate your life expectancy and show you how much time you have left, while others provide daily quotes or prompts for reflection on mortality. While these tools might seem morbid at first glance, they can be powerful motivators for living intentionally.
Video Source: Daily Stoic YouTube Channel
Social media, often criticized for promoting shallow engagement, can be repurposed for this practice. You might follow accounts that share Stoic wisdom or join online communities dedicated to discussing Stoic practices, including Memento Mori. I've found that engaging with these communities can provide valuable insights and support in maintaining a Stoic practice.
Digital journaling apps can be used to record your thoughts on mortality and track how this awareness impacts your daily life and decisions. This digital record can be a powerful tool for self-reflection and personal growth.
Remember, the goal isn't to become obsessed with death, but to use these digital tools mindfully to enhance your appreciation of life and focus on what truly matters to you. It's about striking a balance between awareness of mortality and fully engaging with life.
Negative Visualization
Negative visualization, or premeditatio malorum, is a Stoic technique that involves imagining worst-case scenarios. While it might sound counterintuitive, this practice can actually foster gratitude, resilience, and preparedness.
The idea is to regularly contemplate losing the things you value - your job, your health, your relationships. This doesn't mean dwelling on these scenarios, but briefly considering them. By imagining these losses, you cultivate gratitude for what you currently have. It's a powerful reminder of the good in our lives that we often take for granted.
This practice also helps build resilience. By mentally preparing for challenges, you're better equipped to handle them if they do occur. It's like a mental fire drill, preparing you for potential difficulties. I've found that when I've practiced negative visualization, I'm less thrown off balance when real challenges arise.
Negative visualization can be particularly useful in our age of constant comparison. It helps counteract the "hedonic treadmill" effect, where we quickly adapt to improvements in our circumstances and always want more. By imagining the loss of what we have, we can more fully appreciate our current situation.
Research published in the Journal of Personality and Social Psychology suggests that negative visualization can increase happiness and life satisfaction by enhancing appreciation for one's current circumstances. This scientific backing adds weight to the ancient Stoic practice.
To practice, set aside a few minutes each day. Choose an aspect of your life - your job, a relationship, your health - and briefly imagine losing it. Then, shift your focus to appreciating its presence in your life. The goal isn't to induce anxiety, but to foster gratitude and preparedness.
Applying Negative Visualization to Career and Relationships
Negative visualization can be a powerful tool in professional and personal contexts. It can highlight areas for professional development and motivate expression of appreciation in relationships.
In your career, imagine losing your job or facing a major setback. How would you cope? What skills would you rely on? This exercise can highlight areas for professional development and increase your appreciation for your current position. It might also motivate you to diversify your skills or build a stronger professional network.
Imagine a software developer who practices negative visualization. They might envision losing their job due to rapid advancements in AI. This exercise could motivate them to continuously update their skills, diversify their expertise, and build a strong professional network. As a result, they become more resilient to potential career setbacks and more appreciative of their current position.
For relationships, visualize life without a loved one. This isn't about inducing anxiety, but about recognizing the value of your connections. It can motivate you to express appreciation more often and resolve conflicts more readily. I've found that this practice has made me more patient and understanding in my relationships, as I'm acutely aware of how precious they are.
This practice can also help in setting priorities. By imagining the loss of various aspects of your life, you might gain clarity on what truly matters to you. This can guide your decision-making and help you allocate your time and energy more effectively.
Remember, the goal is brief, purposeful reflection, not prolonged worry. Use this technique as a tool for gratitude and growth, not as a source of stress. It's about striking a balance between preparedness and appreciation.
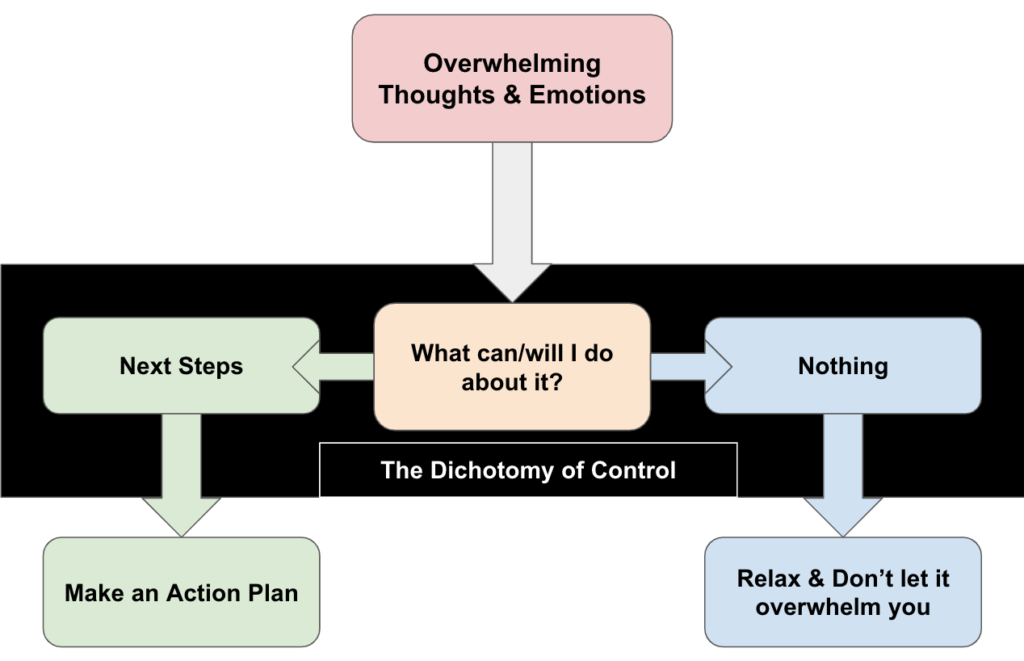
The Dichotomy of Control
The dichotomy of control is a fundamental Stoic concept that involves distinguishing between what we can and cannot influence. Mastering this principle can lead to reduced stress, improved focus, and greater peace of mind.
At its core, this concept teaches us to focus our energy on what we can control - primarily our thoughts, actions, and reactions - and accept what we can't control, which includes most external events and other people's behaviors.
Source: mindandpractice.com
Applying this principle doesn't mean becoming passive. Instead, it's about directing our efforts where they can have the most impact. We act on what we can influence while accepting the rest with equanimity.
This approach can be liberating. By letting go of what's beyond our control, we free up mental and emotional resources for more productive pursuits. I've found that when I focus on what I can control, I feel more empowered and less anxious, even in challenging situations.
Practicing the dichotomy of control involves regular self-reflection. When faced with a situation, ask yourself: "What aspects of this can I influence?" Focus your energy there, and practice acceptance for the rest.
Control in the Age of Social Media and Information Overload
Applying the Stoic principle of the dichotomy of control to our digital lives can help manage overwhelm and maintain focus on what truly matters. In an era of constant connectivity and information bombardment, this principle becomes increasingly valuable.
Social media often causes stress over things beyond our control - others' opinions, the number of likes we receive, or the curated images of others' lives. Applying the dichotomy of control means focusing on what we can influence: the content we create, the time we spend online, and our reactions to what we see.
Information overload can be addressed similarly. We can't control the vast amount of information available, but we can choose what we consume, how we verify it, and how we use it. This selective approach can lead to a more balanced and less stressful digital experience.
A study by the Royal Society for Public Health found that social media use is associated with increased rates of anxiety, depression, and poor sleep. Applying Stoic principles could help mitigate these negative effects.
Consider creating boundaries for your digital engagement. This might involve setting specific times for checking social media or news, or curating your feeds to align with your values and goals. I've found that implementing these boundaries has significantly reduced my digital stress and improved my overall well-being.
Remember, the goal isn't to disconnect entirely, but to engage mindfully. By focusing on what you can control in your digital life, you can use these tools more effectively while maintaining your peace of mind.
Modern Stoicism: Adaptations and Critiques
As Stoicism gains popularity in contemporary society, it's being adapted to address modern issues. This resurgence has led to both innovative applications and thoughtful critiques of the philosophy.
Modern Stoicism often blends ancient wisdom with insights from psychology and neuroscience. This interdisciplinary approach has led to new applications in areas like stress management and personal development. It's fascinating to see how ancient principles are being validated and enhanced by modern scientific understanding.
Contemporary Stoics are also grappling with how to apply the philosophy to current ethical issues, from climate change to social justice. This has led to debates about the scope and limits of Stoic ethics in addressing systemic problems.
Critics argue that some modern interpretations of Stoicism oversimplify the philosophy, turning it into a self-help tool stripped of its ethical core. Others question whether an ancient philosophy can adequately address the complexities of modern life.
A survey by the Modern Stoicism organization found that 96% of participants reported improved life satisfaction after practicing Stoic principles for just one week. While this statistic is impressive, it's important to approach such findings critically and consider potential biases or limitations in the study.

Source: thegeekyleader.com
Despite these critiques, many find value in adapting Stoic principles to contemporary challenges. The key lies in thoughtful application, balancing fidelity to core Stoic ideas with openness to new insights and contexts.
Stoicism in Leadership and Business
Stoic principles are increasingly being applied in corporate environments and leadership training. This trend reflects a growing recognition of the value of philosophical wisdom in professional settings.
In the business world, Stoicism's emphasis on emotional regulation and focus on what's within one's control resonates strongly. Leaders are finding these principles helpful in managing stress, making decisions under pressure, and maintaining ethical standards.
Some companies are incorporating Stoic-inspired practices into their corporate culture. This might include mindfulness sessions, ethics training based on Stoic virtues, or leadership retreats focused on Stoic principles.
Stoicism's focus on character over external success aligns well with modern ideas about authentic leadership. It encourages leaders to prioritize integrity and long-term thinking over short-term gains.
A Harvard Business Review study found that CEOs who practiced mindfulness and emotional regulation, key aspects of Stoicism, were rated as more effective leaders by their employees. This research underscores the practical benefits of Stoic-inspired leadership practices.
However, there's a risk of oversimplification or misapplication. It's crucial to understand Stoicism deeply rather than cherry-picking ideas out of context. Effective implementation requires a nuanced understanding of the philosophy and its application in modern contexts.
Case Studies: Stoic CEOs and Their Impact
Examining real-world examples of business leaders who have successfully incorporated Stoic practices can provide valuable insights into the practical application of this philosophy in high-pressure environments.
One notable example is James Stockdale, a former US Navy vice admiral who credited Stoic philosophy with helping him survive as a prisoner of war. Later, he applied these principles in his leadership roles in business and academia. Stockdale's experience demonstrates how Stoic practices can provide resilience and clarity in even the most challenging leadership situations.
In the tech world, Twitter co-founder Jack Dorsey has spoken about his Stoic practices, including meditation and journaling. He's noted how these habits help him manage the stresses of running a major tech company.
Massimo Pigliucci, a professor of philosophy, has written extensively about applying Stoic principles in his academic career and personal life. His work bridges the gap between ancient wisdom and modern professional challenges.
According to a survey by TalentSmart, CEOs who score high in emotional intelligence (a quality often associated with Stoic practices) outperform their peers, generating an average of $1.5 million more in profit annually. While this statistic is impressive, it's important to consider other factors that might contribute to this performance difference.
These examples illustrate how Stoic principles can be applied across various leadership contexts, from high-stress military situations to fast-paced tech environments and academic settings. They demonstrate the versatility and enduring relevance of Stoic philosophy in modern leadership.
Stoicism and Mental Health
The intersection of Stoic practices with modern psychology and therapy is an area of growing interest. Many mental health professionals are finding value in Stoic techniques, recognizing their potential to complement existing therapeutic approaches.
Stoicism's emphasis on managing one's thoughts and perceptions aligns well with cognitive-behavioral approaches to therapy. Both encourage examining and reframing our thoughts to improve emotional well-being.
The philosophy's focus on acceptance of what's beyond our control resonates with mindfulness-based therapies. Both encourage a non-judgmental awareness of our thoughts and experiences.
Source: pinterest.com
Some therapists are directly incorporating Stoic exercises into their practice. This might include negative visualization to combat anxiety or Stoic journaling to process emotions. I've personally found that integrating Stoic practices into my own mental health routine has provided an additional layer of resilience and self-awareness.
A study published in the Journal of Cognitive Psychotherapy found that integrating Stoic principles into cognitive-behavioral therapy resulted in significant improvements in patients' emotional regulation and resilience. This research suggests that Stoic practices could be a valuable complement to traditional therapeutic approaches.
However, it's important to note that Stoicism isn't a replacement for professional mental health care. Rather, it can be a complementary tool in a broader approach to mental wellness. As with any philosophical or therapeutic approach, it's crucial to apply Stoic principles thoughtfully and in consultation with mental health professionals when dealing with serious mental health issues.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy and Stoicism
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) has strong roots in Stoic philosophy. This connection offers intriguing possibilities for enhancing therapeutic approaches and personal growth practices.
CBT's core principle - that our thoughts influence our emotions and behaviors - echoes the Stoic emphasis on the power of perception. Both approaches encourage examining and reframing our thoughts to create more realistic and helpful ways of thinking.
Techniques like cognitive restructuring in CBT have clear parallels with Stoic practices of challenging our judgments and perceptions. Both aim to create more realistic and helpful ways of thinking about life's challenges.
Some therapists are explicitly combining CBT with Stoic philosophy, creating what's sometimes called "Stoic therapy." This approach uses Stoic exercises and principles within a CBT framework, offering a unique blend of ancient wisdom and modern psychological techniques.
A meta-analysis published in the Journal of Rational-Emotive & Cognitive-Behavior Therapy found that CBT interventions incorporating Stoic principles showed enhanced effectiveness in treating anxiety and depression compared to standard CBT alone. This research suggests that the integration of Stoic ideas could potentially enhance the efficacy of established therapeutic approaches.
While the connection is strong, it's worth noting that CBT has evolved significantly beyond its Stoic roots, incorporating insights from various psychological theories and research. The modern practice of CBT is a sophisticated therapeutic approach that, while influenced by Stoic ideas, stands on its own as a well-researched and effective treatment for many mental health issues.
Criticisms and Limitations of Stoicism
While Stoicism offers valuable insights, it's not without its critics. Examining these critiques can provide a more balanced understanding of the philosophy and its potential limitations in addressing modern complexities.
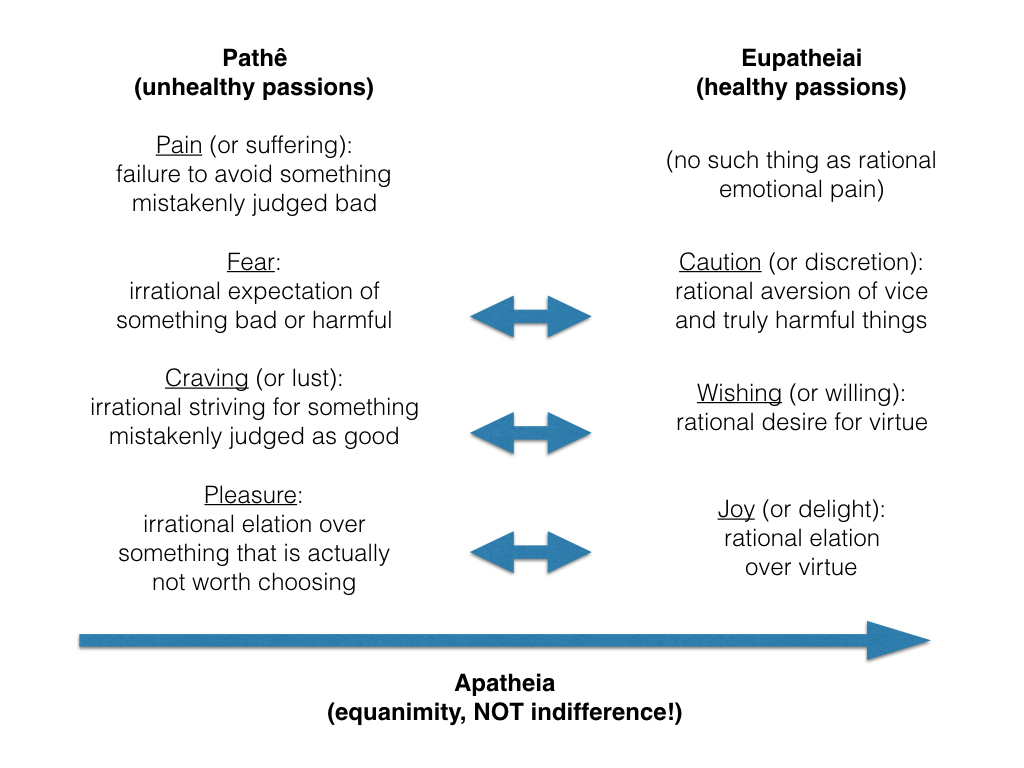
One frequent criticism is that Stoicism can promote emotional suppression. Critics argue that the emphasis on controlling one's reactions might lead to unhealthy emotional repression. It's a valid concern that requires careful consideration in the application of Stoic principles.
Another critique is that Stoicism's focus on individual virtue might downplay the importance of systemic change. Some argue that this could lead to complacency in the face of social injustices. This criticism highlights the need to balance personal virtue with active engagement in societal issues.
There's also debate about whether Stoicism's emphasis on accepting fate could lead to passivity. Critics worry this might discourage proactive problem-solving or activism. It's important to distinguish between acceptance and resignation, and to understand how Stoic acceptance can actually empower action.
Some find Stoicism's rationalistic approach limiting, arguing that it doesn't fully account for the complexity of human emotions and experiences. This critique reminds us of the importance of balancing reason with emotional intelligence.
A study in the Journal of Personality found that individuals who scored high on measures of Stoic endurance also reported lower levels of emotional expressiveness, raising questions about potential drawbacks of Stoic practices. This research underscores the need for a nuanced approach to applying Stoic principles, particularly in emotional contexts.
It's important to engage with these critiques thoughtfully. Many modern Stoics are working to address these concerns, adapting the philosophy to better meet contemporary challenges. By acknowledging and grappling with these limitations, we can develop a more robust and nuanced understanding of Stoicism's place in modern life.
Stoicism and Social Justice
The application of Stoic principles to issues of social justice is a topic of ongoing debate. This discussion highlights both the potential contributions and limitations of Stoic philosophy in addressing systemic inequalities and collective action.
Stoicism's emphasis on personal virtue and individual responsibility can be seen as both a strength and a limitation in addressing social justice issues. On one hand, it encourages personal accountability and ethical action. On the other, critics argue it might not adequately address systemic problems.
Some modern Stoics are exploring how the philosophy's concept of cosmopolitanism - the idea of being a citizen of the world - can inform approaches to global justice and equality. This perspective encourages a broader view of social responsibility that extends beyond national or cultural boundaries.
The Stoic virtue of justice, which includes fairness and benevolence, provides a framework for engaging with social issues. However, there's debate about how to balance this with the Stoic focus on what's within our control.
Consider the case of a Stoic-inspired activist working on climate change. They might use Stoic principles to maintain emotional resilience in the face of slow progress and setbacks. At the same time, they could draw on the Stoic concept of cosmopolitanism to argue for global cooperation on environmental issues. This example shows how Stoic ideas can be adapted to modern social justice contexts, while also highlighting the need to balance individual virtue with collective action.
Ultimately, the application of Stoicism to social justice requires careful consideration and adaptation. It involves balancing personal virtue with collective responsibility, and individual action with systemic change. As we grapple with complex social issues, Stoic principles can offer valuable insights, but they must be applied thoughtfully and in conjunction with other frameworks for social change.
The Future of Stoicism
As we look ahead, Stoicism continues to evolve and find new applications. The philosophy's potential role in addressing future challenges and shaping ethical frameworks in emerging technologies and societal changes is a subject of growing interest.
Stoicism's emphasis on resilience and adaptability positions it well to help individuals navigate an increasingly uncertain future. Its principles could prove valuable in coping with rapid technological change and environmental challenges. I've found that Stoic practices have helped me maintain perspective and focus in the face of constant change and uncertainty in my own life and career.
In the realm of technology ethics, Stoic ideas about virtue and human flourishing could inform discussions about AI development and the ethical use of emerging technologies. As we grapple with the implications of advanced AI and other transformative technologies, Stoic principles might offer a valuable ethical framework.
As global challenges become more complex, Stoicism's cosmopolitan outlook might offer a framework for fostering global cooperation and understanding. The idea of being a citizen of the world resonates strongly in our interconnected global society.
A report by the World Economic Forum highlighted Stoicism as one of the philosophical approaches that could help shape ethical frameworks for emerging technologies like artificial intelligence and biotechnology. This recognition underscores the potential relevance of Stoic principles in addressing future technological and ethical challenges.
Source: linkedin.com
The future of Stoicism likely involves continued dialogue between ancient wisdom and modern insights. This could lead to new interpretations and applications of Stoic principles in areas we can't yet foresee. It's an exciting prospect that keeps the philosophy dynamic and relevant.
Stoicism in the Digital Age
The digital revolution presents both challenges and opportunities for Stoic practice. Navigating the complexities of our hyper-connected world through a Stoic lens can offer valuable insights for ethical development and mindful use of technology.
In the realm of social media, Stoic ideas about impression management and the dichotomy of control can help users navigate the pressures of online life more mindfully. I've found that applying these principles has significantly reduced my digital anxiety and improved my overall online experience.
For developers and tech leaders, Stoic ethics could inform decision-making about data privacy, algorithmic fairness, and the societal impacts of new technologies. As we grapple with the ethical implications of AI and other emerging technologies, Stoic principles of virtue and human flourishing could provide a valuable framework.
The Stoic emphasis on continuous learning aligns well with the need for adaptability in our rapidly changing digital landscape. It encourages a mindset of lifelong growth and skill development, which is crucial in an era of constant technological advancement.
A survey by the Pew Research Center found that 64% of Americans believe social media has a mostly negative effect on the way things are going in the country. Stoic principles could offer a framework for more mindful and ethical engagement with these platforms, potentially mitigating some of these negative effects.
As we grapple with issues like digital addiction and information overload, Stoic practices of self-discipline and focused attention could prove increasingly valuable. These ancient techniques, when adapted to our modern context, offer powerful tools for maintaining balance in our digital lives.
Stoic Ethics for Artificial Intelligence
As AI systems become more advanced and ubiquitous, incorporating ethical frameworks into their development is crucial. Stoic virtues and principles could potentially inform AI decision-making algorithms, offering a unique perspective on machine ethics.
The Stoic emphasis on rationality and ethical decision-making could provide a valuable framework for developing AI systems that make fair and beneficial choices. Imagine an AI system that not only processes data efficiently but also considers the ethical implications of its decisions through a Stoic lens.
Stoic virtues like wisdom, justice, courage, and temperance could be translated into guiding principles for AI behavior, helping to ensure that these systems act in ways that promote human flourishing. This could lead to AI that's not just intelligent, but also ethically aligned with human values.
The Stoic concept of cosmopolitanism - viewing all humans as part of a global community - could inform AI systems designed to make decisions that consider the broader impact on humanity, not just narrow objectives. This perspective could be particularly valuable in developing AI for global challenges like climate change or public health crises.
A study published in the journal AI & Society proposed that incorporating Stoic ethical principles into AI decision-making frameworks could lead to more robust and ethically aligned artificial intelligence systems. This research suggests a promising avenue for integrating ancient wisdom with cutting-edge technology.
However, translating human ethical systems into AI algorithms presents significant challenges. It requires careful consideration of how to interpret and apply these principles in non-human decision-making processes. The complexity of this task highlights the need for interdisciplinary collaboration between philosophers, ethicists, and AI researchers.
Environmental Stoicism
Stoic philosophy offers intriguing perspectives on addressing environmental challenges. The Stoic view of nature as a rational, interconnected system aligns well with modern ecological understanding, potentially fostering a deeper appreciation for environmental stewardship.
Stoicism's emphasis on virtue and duty could motivate individuals to take personal responsibility for their environmental impact, even in the face of global challenges. I've found that applying Stoic principles has made me more mindful of my consumption habits and more committed to sustainable practices.
The Stoic practice of voluntary discomfort could be applied to adopting more sustainable, but potentially less convenient, lifestyle choices. This might involve choosing public transportation over driving or reducing meat consumption, decisions that align with environmental goals but require personal sacrifice.
A report by the United Nations Environment Programme highlighted philosophical approaches, including Stoicism, as potential frameworks for promoting sustainable lifestyles and environmental stewardship. This recognition underscores the potential of Stoic principles to contribute to environmental solutions.
However, critics might argue that Stoicism's focus on personal virtue isn't sufficient to address systemic environmental issues. Balancing individual action with advocacy for larger-scale changes remains a challenge. It's crucial to consider how Stoic principles can complement and support broader environmental initiatives and policy changes.
Stoic Minimalism and Sustainable Consumption
Stoic principles of temperance and finding happiness in virtue rather than material possessions align well with eco-friendly lifestyle choices. This connection offers interesting possibilities for promoting sustainable consumption patterns.
Stoicism's emphasis on distinguishing between needs and wants can guide more mindful consumption habits. This aligns with minimalist approaches to reducing waste and overconsumption. By questioning our desires and focusing on what truly adds value to our lives, we can make more environmentally conscious choices.
The Stoic practice of negative visualization can help cultivate gratitude for what we have, potentially reducing the drive for unnecessary purchases. This mental exercise can be a powerful tool in combating the constant pressure to consume that characterizes much of modern society.
Stoic ideas about finding fulfillment in virtue rather than external goods can support a shift away from consumerism towards more sustainable lifestyles. This perspective challenges the notion that happiness comes from accumulating possessions, encouraging a focus on personal growth and ethical living instead.
A study in the Journal of Consumer Research found that individuals who practiced mindfulness and gratitude, key aspects of Stoic philosophy, reported lower levels of materialistic values and higher levels of life satisfaction. This research suggests that Stoic-inspired practices could contribute to more sustainable consumption patterns.
However, it's important to balance individual choices with awareness of broader systemic issues. Stoic minimalism should complement, not replace, efforts for larger-scale environmental change. The challenge lies in applying these principles effectively at both personal and societal levels.
Stoicism and Global Citizenship
Stoic cosmopolitanism offers a framework for approaching global challenges and fostering cross-cultural understanding. In our interconnected world, this aspect of Stoic philosophy seems particularly relevant and timely.
The Stoic idea of being a "citizen of the world" resonates strongly in our globalized era. It encourages thinking beyond national boundaries and considering the welfare of all humanity. This perspective can be valuable in addressing global issues that require international cooperation.
Stoic emphasis on common humanity and universal reason can promote empathy and understanding across cultural divides. By focusing on our shared human experience, Stoicism offers a philosophical basis for bridging cultural and ideological gaps.
In addressing global challenges like climate change or poverty, Stoic principles of duty and justice can motivate individuals to take action, even when the problems seem overwhelming. This sense of global responsibility aligns well with the needs of our interconnected world.
A survey by the Pew Research Center found that 60% of people across 14 advanced economies believe that global cooperation is extremely or very important for dealing with major challenges like climate change and pandemics. This aligns well with Stoic ideas of global citizenship and collective responsibility.
However, balancing Stoic cosmopolitanism with respect for cultural diversity and local identities remains a complex challenge in practice. It's crucial to consider how Stoic principles can be applied in a way that respects and celebrates cultural differences while promoting global cooperation.
Stoic Diplomacy in International Relations
Stoic principles offer intriguing possibilities for enhancing diplomatic practices and conflict resolution. The philosophy's emphasis on reason, emotional regulation, and ethical conduct could potentially inform more effective approaches to international relations.
The Stoic emphasis on reason and emotional regulation could inform more measured approaches to international negotiations, potentially reducing escalations driven by reactive emotions. Imagine diplomats trained in Stoic practices, able to maintain composure and clarity in high-stakes negotiations.
Stoic cosmopolitanism could encourage diplomats to consider the global impact of their decisions, not just national interests. This broader perspective might lead to more collaborative solutions to international challenges, fostering a sense of shared global responsibility.
The Stoic practice of perspective-taking could enhance empathy in diplomatic interactions, helping negotiators better understand and address the concerns of other nations. This skill could be particularly valuable in resolving long-standing conflicts or cultural misunderstandings.
Consider a hypothetical diplomatic negotiation over water rights between two neighboring countries. A diplomat trained in Stoic principles might approach the situation by first practicing emotional regulation to remain calm and objective. They would then apply the Stoic concept of cosmopolitanism, considering the long-term benefits for both nations and the wider region, rather than seeking a narrow "win" for their own country. Finally, they might use the Stoic practice of perspective-taking to better understand the other nation's position, fostering empathy and potentially leading to a more mutually beneficial resolution.
However, critics might argue that Stoic detachment could potentially hinder the passion sometimes necessary for advocating strongly for human rights or urgent global issues. Balancing Stoic principles with the need for decisive action in critical situations remains a challenge in applying this philosophy to diplomacy.
Learnings Recap
As we conclude our exploration of Stoicism in 2024, let's recap the key insights and practical applications we've discovered. This summary will help solidify your understanding and provide a roadmap for incorporating Stoic principles into your life.
Source: iep.utm.edu
- Stoicism offers a practical framework for cultivating resilience, ethical living, and inner peace in our modern world.
- Core Stoic practices like negative visualization, the dichotomy of control, and Memento Mori can be adapted to address contemporary challenges.
- Modern applications of Stoicism extend to areas like business leadership, mental health, environmental sustainability, and global citizenship.
- While Stoicism provides valuable tools for personal growth, it's important to engage critically with the philosophy, acknowledging its limitations and potential critiques.
- The future of Stoicism involves ongoing dialogue between ancient wisdom and modern insights, particularly in areas like technology ethics and global cooperation.
As you move forward, I encourage you to experiment with Stoic practices in your daily life. Start small, perhaps with a morning meditation or journaling session. Pay attention to how these practices impact your thoughts, emotions, and actions over time.
Remember, Stoicism isn't about achieving perfection, but about continuous improvement and striving to live virtuously. Be patient with yourself as you explore these ideas and practices.
Lastly, consider joining a community of modern Stoics, either online or in person. Discussing these ideas with others can deepen your understanding and provide support in your practice.
As we face the complexities of life in 2024 and beyond, Stoicism offers timeless wisdom that can help us navigate challenges with grace, purpose, and resilience. May your journey with Stoic principles be enlightening and transformative.
Further Reading
Staying Grounded with Stoicism offers valuable insights on how to apply Stoic principles to maintain focus and resilience in our daily lives. By embracing these timeless teachings, we can learn to differentiate between what we can and cannot control, allowing us to direct our energy more effectively.
One of the core tenets of Stoicism is the pursuit of self-mastery. Becoming the Captain of Your Soul provides practical tips on how to develop this crucial skill through Stoic practices. By cultivating virtues such as wisdom, justice, courage, and self-control, we can take charge of our thoughts and actions, steering our lives in the direction we choose.
Life inevitably presents us with challenges, but Stoicism equips us with tools to face these difficulties head-on. Confronting Life's Challenges with Stoic Wisdom explores how Stoic principles can help us approach adversity with courage and equanimity. By reframing our perspective and focusing on our response rather than external circumstances, we can maintain inner peace even in turbulent times.
Incorporating these Stoic teachings into our lives can lead to greater resilience, contentment, and personal growth. As we practice these principles, we may find ourselves better equipped to handle life's ups and downs with grace and wisdom.
Get our next quote reflection straight to your inbox 👇
Share with a fellow Stoic 🙏
